Sewage treatment plant monitoring for nitrifying bacteria
*taxes and shipping not included
qPCR sewage treatment plant monitoring for nitrifying bacteria
| Target | DNA |
| Selling unit | 6 Test(s), 12 Test(s), 24 Test(s) |
| Shelf life (from production) | 3 Year(s) |
| Hazardous material | No |

Microscopy 2.0 - The innovation in wastewater analysis
In a biological sewage treatment plant, the process of nitrification, the conversion of nitrogen compounds to nitrate, is used for purification. A certain group of bacteria, the nitrificants, is responsible for the conversion of nitrogen compounds to nitrate. This group includes the ammonium-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and the nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) and nitrotoga.
- Prevention of operational disruptions due to high sensitivity of the method
- Increased efficiency of the system
- Support of root cause investigation in case of malfunction
The PCR - details about the nitrificant population of your plant
Pollution in the millimolar range already has a considerable influence on the nitrificant population and can lead to an inhibition of nitrification. Due to the high sensitivity of the PCR, you can monitor even the smallest changes in your nitrificant population and initiate countermeasures promptly.
Each plant has its own fingerprint
The wastewater treatment plants (A-D) show their own nitrificant composition. The qPCR analysis shows the course of the measurements over a period of 49 days. For this purpose, the individual populations of the nitrifiers, AOB and NOB, as well as, in the case of plant B-D, nitrotoga, are detected with the help of qPCR.
The data were compiled in cooperation with DyeNA Genetics GmbH.
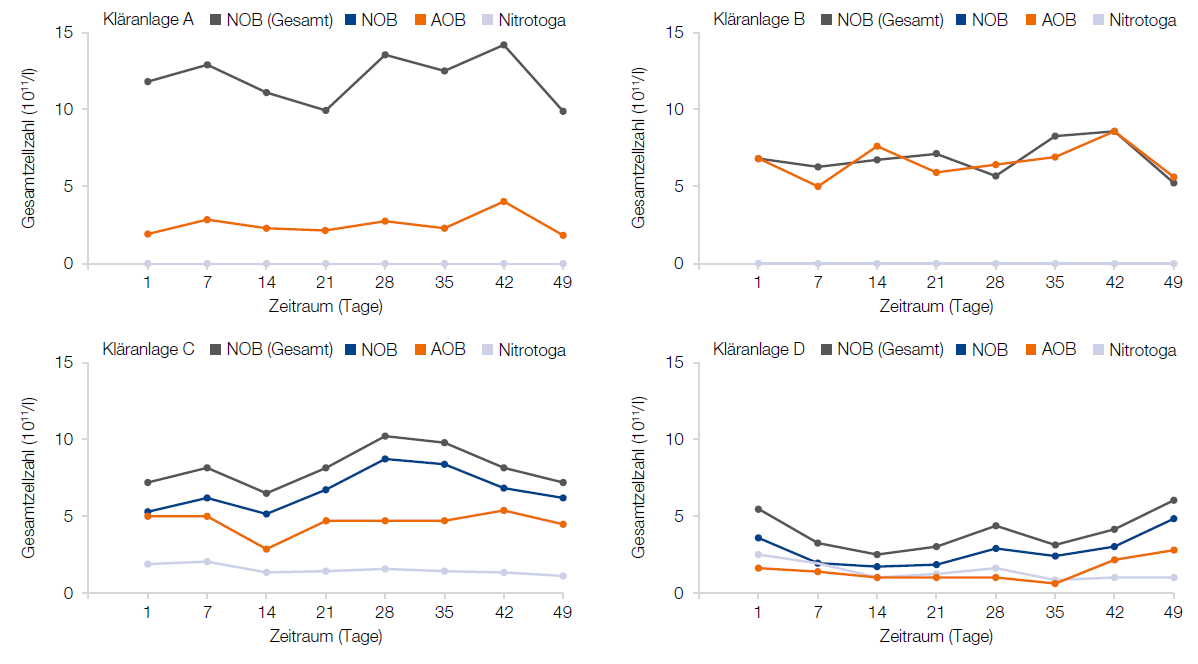
Nitrification: The fingerprint of a wastewater treatment plant
- Detailed insight into the nitrificant population of your plant
- Timely intervention in case of malfunctions
- Monitoring of the nitrificant population to assess structural changes


